This challenge was released on 01/16/2022 from CyberDefenders. You can access the room at https://cyberdefenders.org/labs/86.
This is another blueteam challenge. The skills/tools to be tested and needed to complete this challenge are Autopsy or FTK Imager, dnSpy, VirusTotal, and PowerShell.
I hope you will find my write-up helpful.
- What is the computer hostname?
- vcw65
- What is the Timezone of the compromised machine?
- UTC-8
Check the Registry by going to Windows\System32\config

Click on System, then expand ControlSet001 > Control and click on TimeZoneInformation

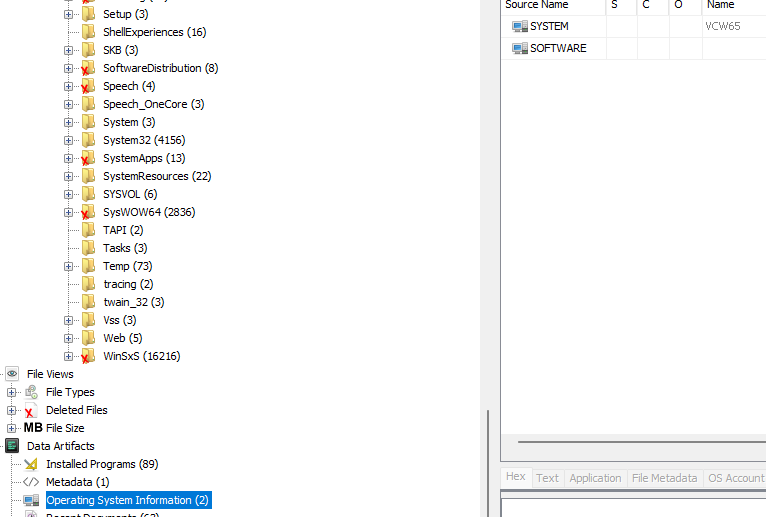
- What is the current build number on the system?
- 14393
Check the Registry by going to Windows\System32\config (See screenshot in question #2)
Click on Software, then expand Microsoft > Windows NT and click on CurrentVersion
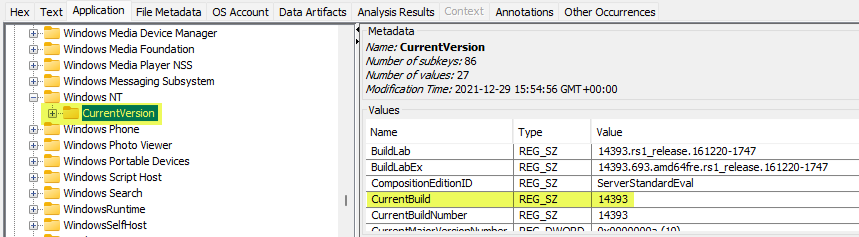
- What is the computer IP?
- 192.168.112.139
Check the Registry by going to Windows\System32\config (See screenshot in question #2)
Click on System, then expand ControlSet001 > Services > Tcpip > Parameters and click on Interfaces
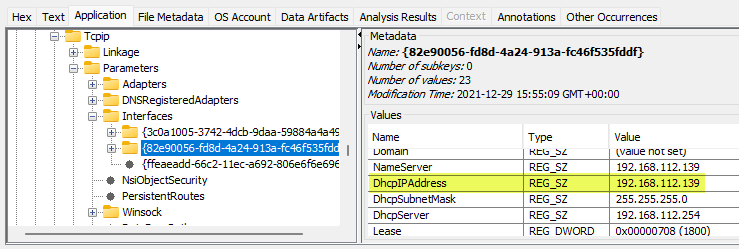
- What is the domain computer was assigned to?
- cyberdefenders.org
Check the Registry by going to Windows\System32\config (See screenshot in question #2)
Click on System, then expand ControlSet001 > Services > Tcpip and click on Parameters
- When was myoussef user created?
- 2021-12-28 06:57:23 UTC
Go to OS Accounts under the Tree Viewer on the left column, then search for the user “myoussef” in the Result Viewer

- What is the user mhasan password hint?
Go to OS Accounts under the Tree Viewer on the left column, then search for the user “mhasan” in the Result Viewer

- What is the version of the VMWare product installed on the machine?
- 6.7.0.40322
Go to Data Artifacts > Installed Programs under the Tree Viewer on the left column, then search for the user “VMWare-vSphereClient” in the Result Viewer

- What is the version of the log4j library used by the installed VMWare produtc?
- 2.11.2
Go to Program Files\VMWare\vCenter Server\common-jars under the Tree Viewer on the left column, then click on log4j-core-2.11.2.jar in the Result Viewer
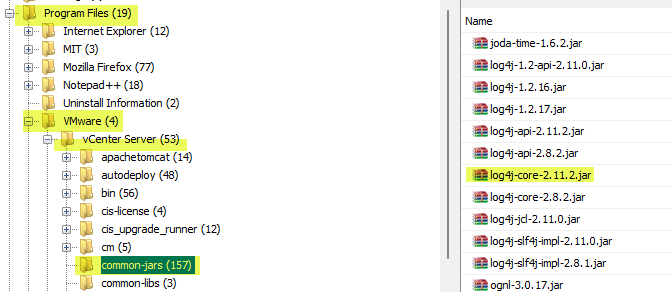
- What is the log4j library log level specified in the configuration file?
- info
Search for the keyword “log4j”, then from the results, click on log4j.properties, then look for the log level in the Content Viewer
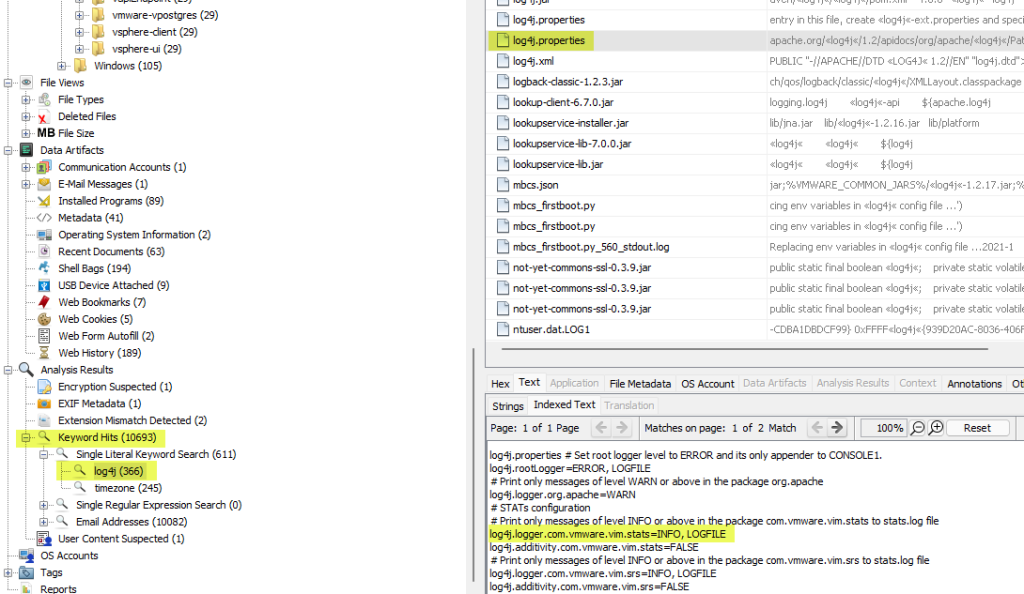
- The attacker exploited log4shell through an HTTP login request. What is the HTTP header used to inject payload?
- X-Forwarded-For
I am familiar with the different HTTP headers used to inject payload, so I just guessed this one out.
- The attacker used the log4shell.huntress.com payload to detect if the VCenter instance is vulnerable. What is the first link of the log4jhuntress payload?
- log4shell.huntress.com:1389/b1292f3c-a652-4240-8fb4-59c43141f55a
Search for the keyword “log4shell.huntress.com”, then click websso.log in the Result Viewer, and you will see the huntress link in the Result Viewer

- When was the first successful login to VSphere WebClient?
- 28/12/2021 20:39:29 UTC
Go to ProgramData\VMWare\vCenterServer\runtime\VMWareSTSService\logs, then click on audit_events.log in the Result Viewer and you will see the timestamp in the Content Viewer

- What is the attacker’s IP address?
- 192.168.112.128
Search for the keyword “log4j”, then from the results, click on audit_events.log, then look for the IP address in the Content Viewer

- What is the port the attacker used to receive the Cobalt Strike reverse shell?
- 1337
Go to Windows\System32\winevt\Logs, then click on Microsft-Windows-PowerShell%4Operational.evtx, then look for a base64 encoded command

Copy the base64 encoded command and decode it using CyberChef using Base64 and Gunzip

Download the decoded command and save it with a .ps1 extension
You can then use Fakenet from Madiant. This tool is used to emulate a network environment to trick the malware we want to analyze into thinking that it is connected to the internet. We can then analyze the network activity of malware. Run the powershell script and analyze the malware’s network activity on fakenet.

- What is the script name published by VMWare to mitigate log4shell vulnerability?
- vc_log4j_mitigator.py
The answer to this question can be obtained by searching the internet
- In some cases, you may not be able to update the products used in your network. What is the system property needed to use to ‘true’ to work around the log4shell vulnerability?
- log4j2.formatMsgNoLookups
The answer to this question can be obtained by searching the internet
- What is the log4j version which contains a patch to CVE-2021-44228?
- 2.15.0
The answer to this question can be obtained by searching the internet
- Removing the JNDIlookup.class may help in mitigating log4shell. What is the sha256 hash of the JNDILookup.class?
- 0f038a1e0aa0aff76d66d1440c88a2b35a3d023ad8b2e3bac8e25a3208499f7e
Extract the log4j-core-2.11.2 from Program Files\VMWare\vCenter Server\VMWare Identity Services\log4j-core-2.11.2.jar

Extract the jar file
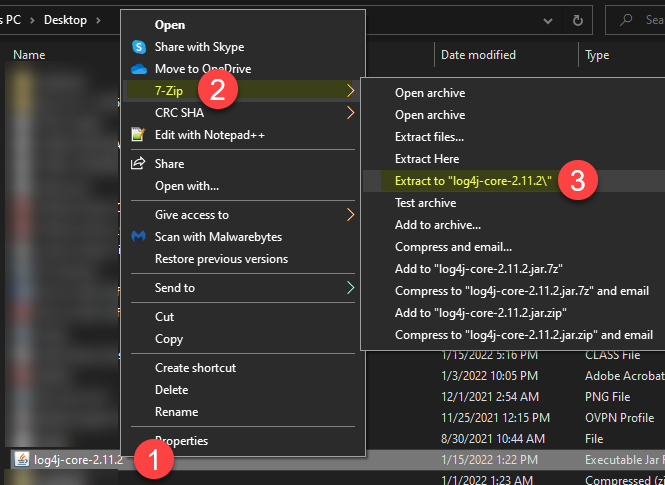
Locate the JNDILookup.class from the extracted jar file and run the command on powershell Get-FileHash -Algoritm sha256 JNDILookup.class

- Analyze JNDILookup.class. What is the value stored in the CONTAINER_JNDI_RESOURCE_PATH_PREFIX variable?
- java:comp/env/
Go to Program Files\VMWare\vCenter Server\cm\lib\log4j-core.jar

- What is the executable used by the attacker to gain persistence?
- baaaackdooor.exe
Go to Users/Administrator.WIN-B633EO9K91M, then click on NTUSER.DAT in the Result Viewer
Expand SOFTWARE > Microsoft > Windows > CurrentVersion, then click on RunOnce

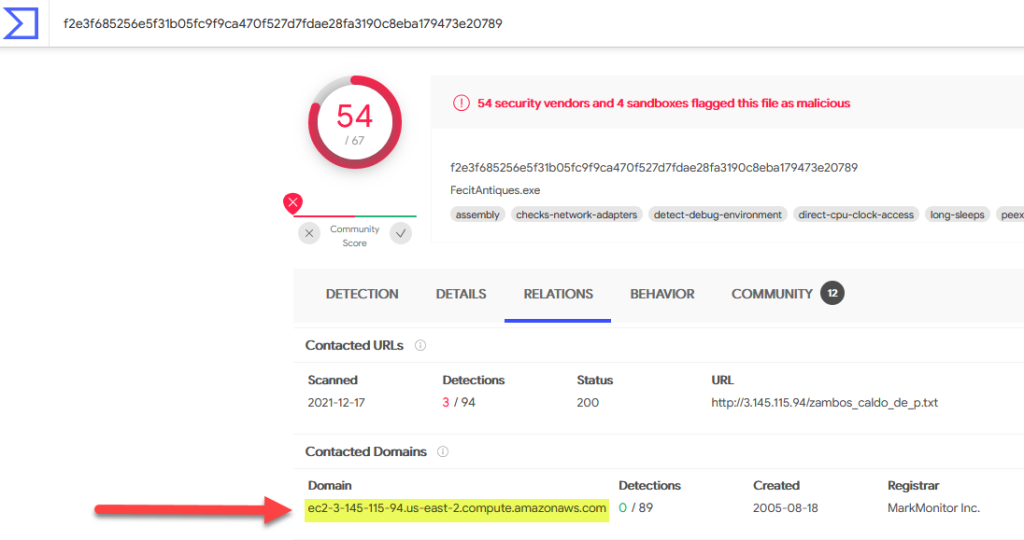
- When was the first submission of the ransomware to VirusTotal?
- 2021-12-11 22:57:01
Search the hash f2e3f685256e5f31b05fc9f9ca470f527d7fdae28fa3190c8eba179473e20789 on VirusTotal, then look for the First Submission under History

- The ransomware downlaods a text file from an external server. What is the key used to decrypt the URL?
- GoaahQrC
Go to https://bazaar.abuse.ch and search using the hash from the previous question.
Download the malware ****Please make sure that you do this in a safe environment because you are downloading REAL malware that will cause damage to your systems****
Upload the malware to dnSpy, then right-click on the new entry on the left column and choose “Go to Entry Point”

Look for the key used for decryption

- What is the ISP that owns the IP that serves the text file?
- amazon
Go back and check the results of your VirusTotal search again
- The ransomware check for extensions to exclude them from the encryption process. What is the second extension the ransomware checks for?
- ini
Happy investigating and hunting. Please subscribe to my blog if you haven’t done so.
Great write up. I think this has good application for other info gathering as well, not just for logforj.
LikeLike