
This room was released on 8/8/2025 and is rated HARD in difficulty. Shout-out to the room creator, hadrian3689. You can access the room at https://tryhackme.com/room/eventhorizonroom.
This is a blueteam challenge. The skills/tools to be tested and needed to complete this challenge are Traffic Analysis using Wireshark, Debugging/Reverse Engineering using dnSpy, and Encoding/Decoding using CyberChef or Terminal.
Scenario: Join Tom and Dom on a quest to find out what happens when you look beyond the Event Horizon. A quest beyond borders, they need you to utilize all your abilities to find the secrets that were taken when they crossed over to the other side.
- The attacker was able to find the correct pair of credentials for the email service. What were they?
- t**.***@************.***:********
- We need to analyze the given pcapng file using Wireshark. The question gave us a good hint to start our analysis. We are asked something related to email service, so, to begin we can filter the network traffic using the POP or SMTP protocols.
- Scroll down until you see the SMTP protocol. Right-click on any of them, then choose Follow > TCP Stream. We will see some base64 entries for the Username and Password, respectively.
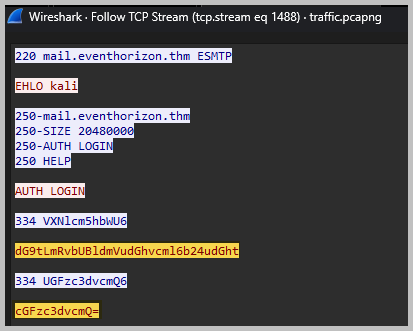
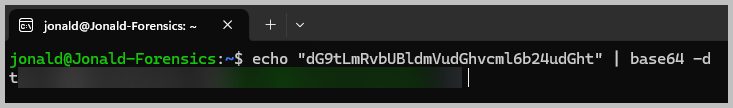
- Open a terminal to decode the data. Type echo “enter_base64_here” | base64 -d
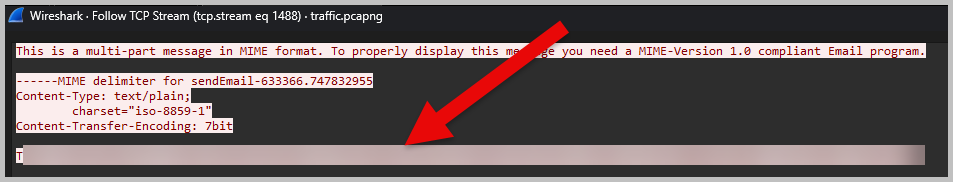
- What was the body of the email that was sent by the attacker?
- T*** * **** **** *** * **** ***** *** **** ** *** ***** **** ** ****** *** **** ***** ** *** ************** *** *** ***** ***
- We can use the same result as we did in step one, following the TCP stream.
- What command initiated the malicious script download?
- I**(***-****** ***.*********).**************(‘****://**.*.*.**/******.***’)
- Again, using the same result as we did in step one, following the TCP stream. Scroll down a little bit more, and we will see another base64-encoded data. Let’s copy it and paste it into CyberChef.
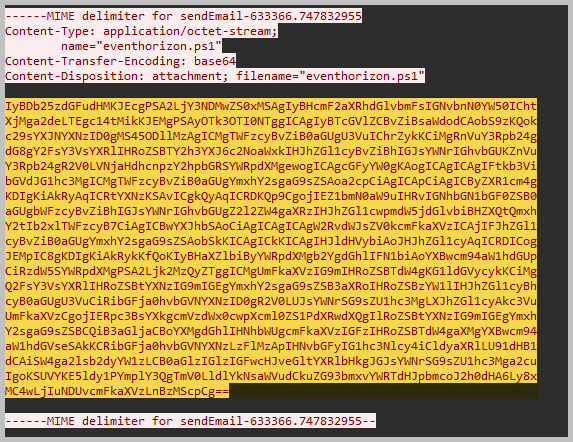
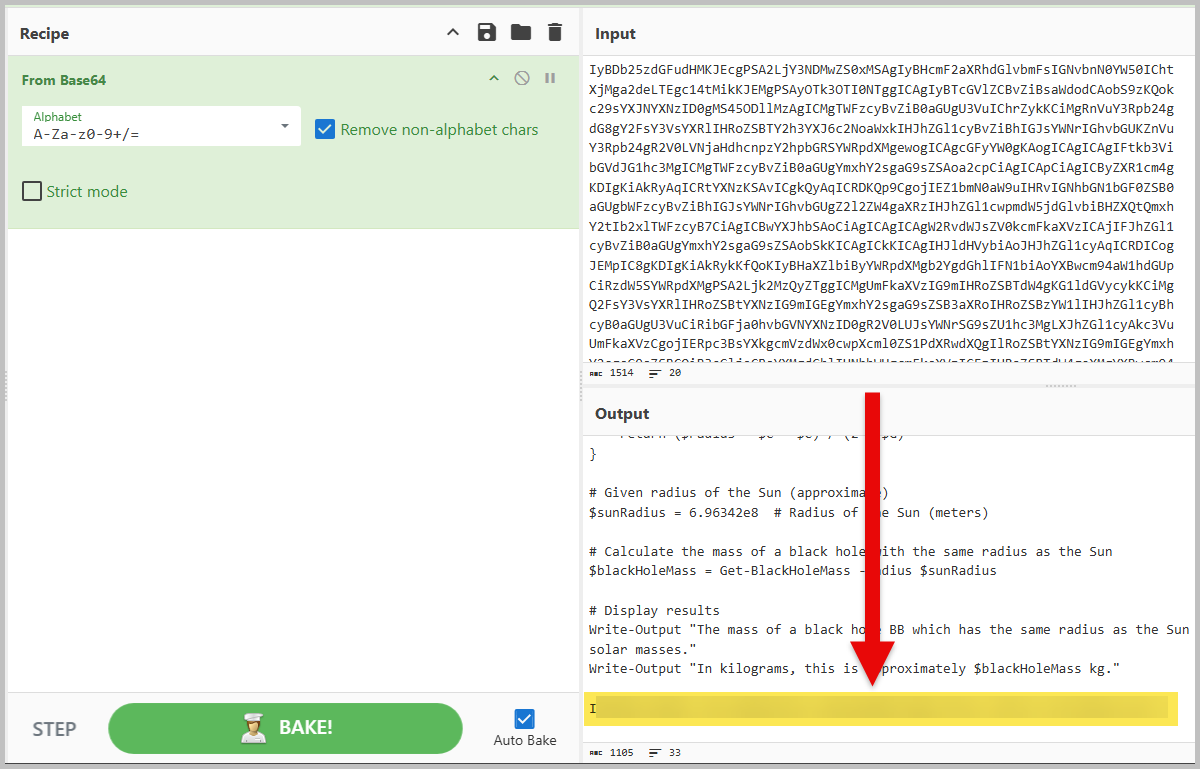
- What is the initial AES key that is used for decrypting the C2 traffic?
- l***************************************/***
- The first 3 questions were the easy part. Questions 4 to 6 jumped to 30 times harder.
- To find the AES key, we need to analyze the malicious script downloaded in question number 3. Inside the malicious script is a base64 payload that was running in memory.

- I asked chatgpt to write me a script to reverse the downloaded malicious script.
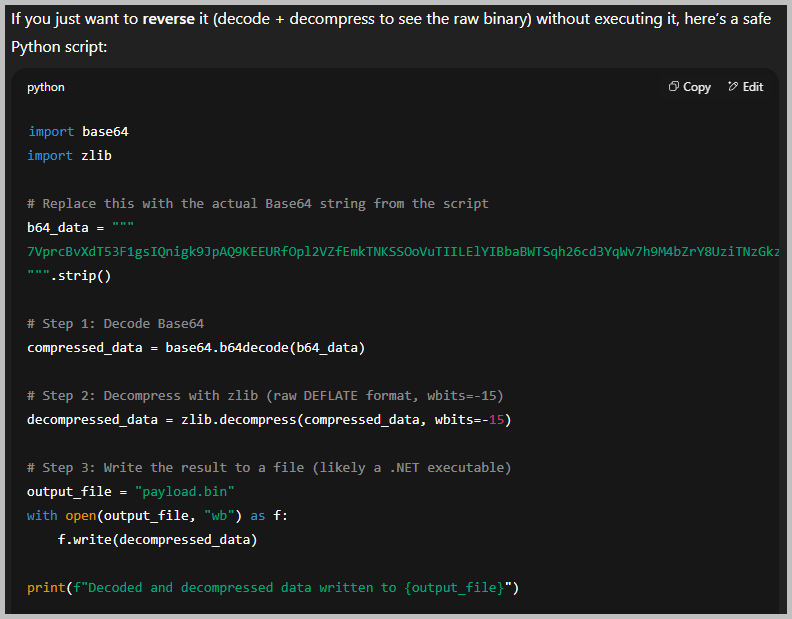
- I named my decoded and decompressed binary as payload.bin. Just for kicks, I queried the hash of payload.bin to check if it is a known binary by using VirusTotal. Run md5sum payload.bin
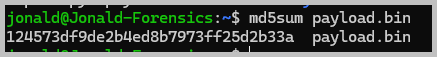
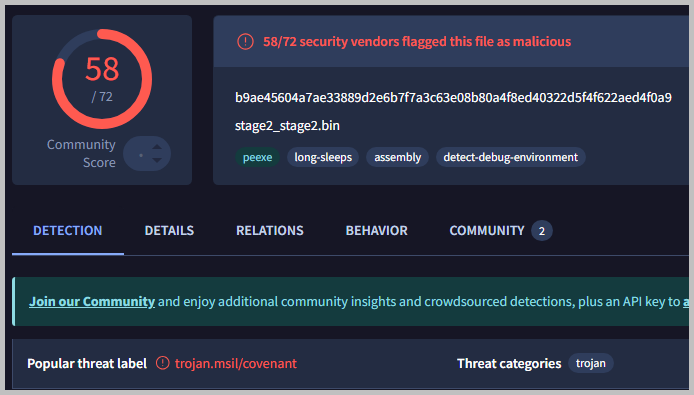
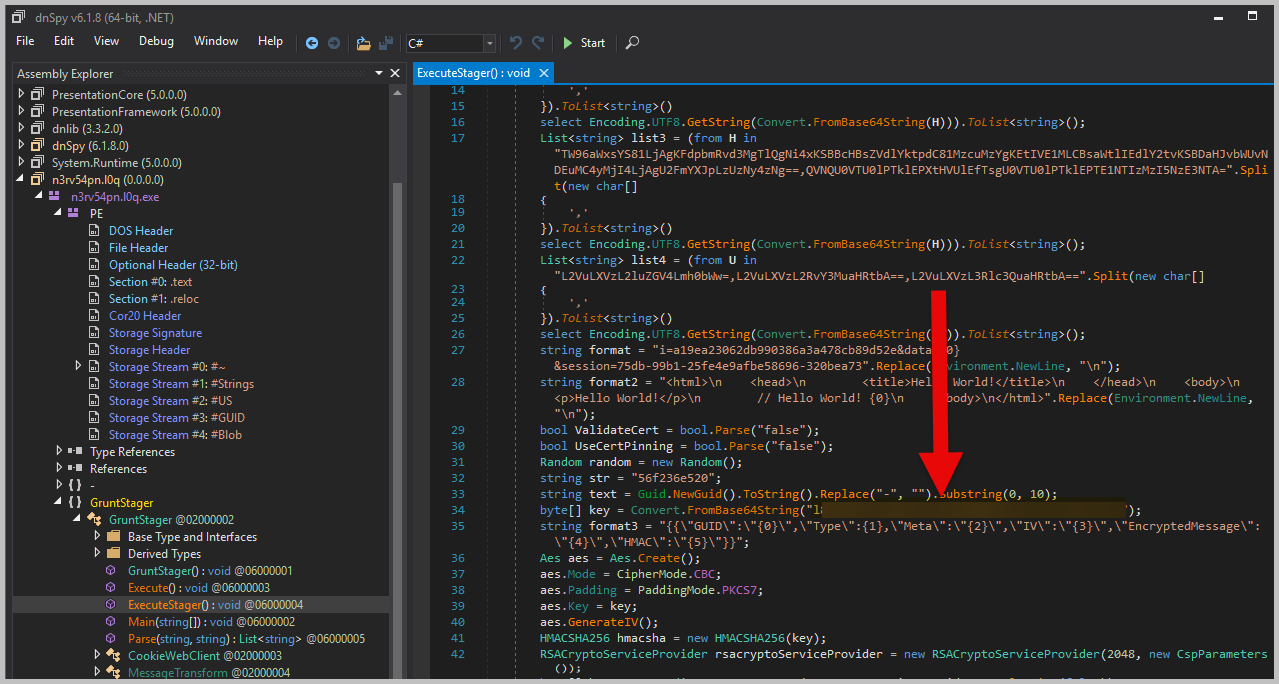
- I then loaded the payload.bin to dnSpy to analyze the script. I was able to locate the initial AES key within the script.
- What is the Administrator NTLM hash that the attacker found?
- 1*******************************
- Checking the hash in question number 4 on VirusTotal proved to be a major step towards solving this challenge. Looking back at the result of the VirusTotal image, we can see that the threat is known as Covenant. Do a little bit of Google search and you will understand what Covenant is used for, and that we need a tool called Covenant Decryptor. I downloaded the repository by running: sudo git clone https://github.com/naacbin/CovenantDecryptor
- Looking at the ReadMe of the Covenant Decryptor, the first step is to extract the modulus from the stage 0 request of the infected host. But before we can proceed with the extraction of the modulus we need to put the traffic all together into a single text file. Go back to Wireshark and find any HTTP packet with GET request to test.html, right-click on it and follow the stream. Now, we need to remove all other data and leave just anything base64 encoded lines. From this:
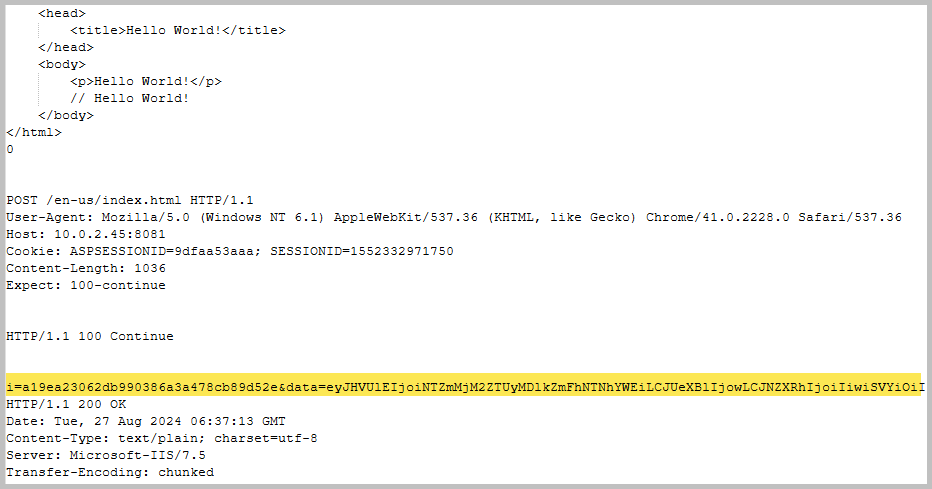
- To this:

- Now, extract the modulus per the instructions from the Covenant Decryptor github page. Run:
python3 decrypt_covenant_traffic.py modulus -i traffic.txt -k "enter_the_initial_AES_key_here" -t base64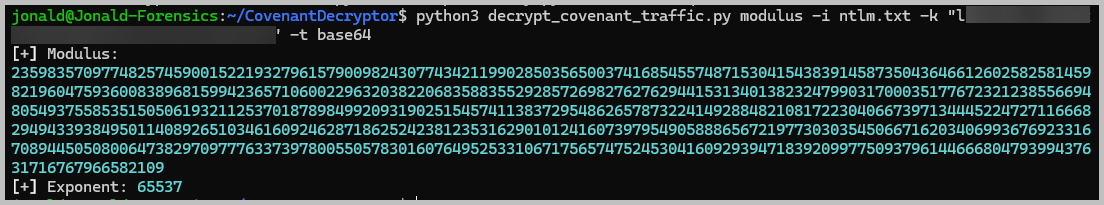
- The next task we need to run, as outlined on the GitHub page, is to retrieve the RSA key from the minidump file of the infected machine. Run:
python3 extract_privatekey.py -i memory.dmp -m enter_the_moduls_here -o ./keys/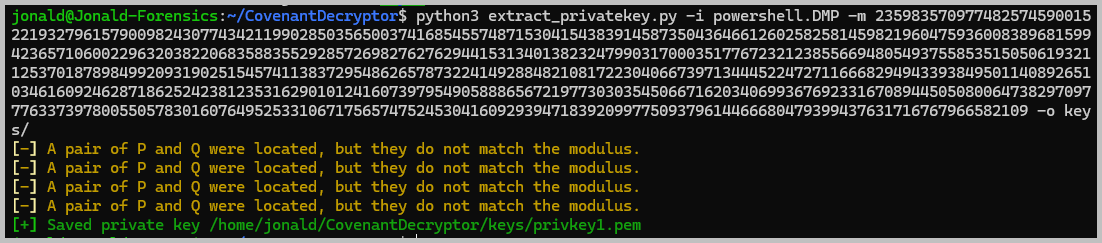
- The next task is to recover the SessionKey from the stage 0 response of the Covenant C2. Again, this can be found on the GitHub page. Run:
python3 decrypt_covenant_traffic.py key -i traffic.txt --key "enter_the_initial_AES_key_here" -t base64 -r privkey1.pem -s 1
- Now that we were able to recover the SessionKey, the last task is to decrypt the Covenant communication. Run:
python3 decrypt_covenant_traffic.py decrypt -i traffic.txt -k "enter_the_new_AES_key_here" -t hex -s 2, and you will see the Administrator NTLM hash.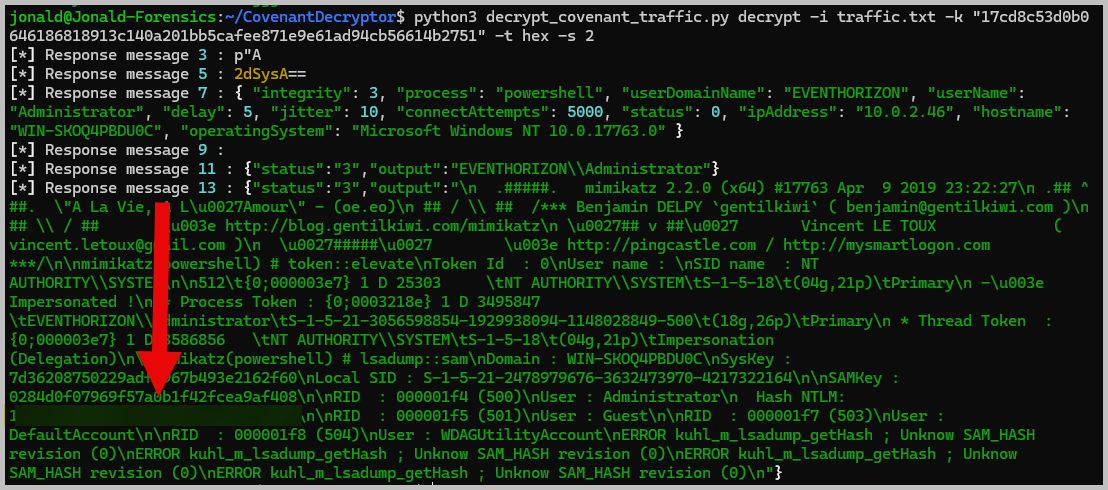
- What is the flag?
- F***{*****_***_*****_***_*****_*******}
- Using the last command from question 5, I redirected the output to a text file. Named the new file as test.txt.

- Then stripped the test.txt of all the HTML code, and left out just the base64 part of the traffic, and saved the new file as flag.txt. I then uploaded flag.txt to CyberChef and used From Base64 and Render Image to decode flag.txt and retrieve the flag.
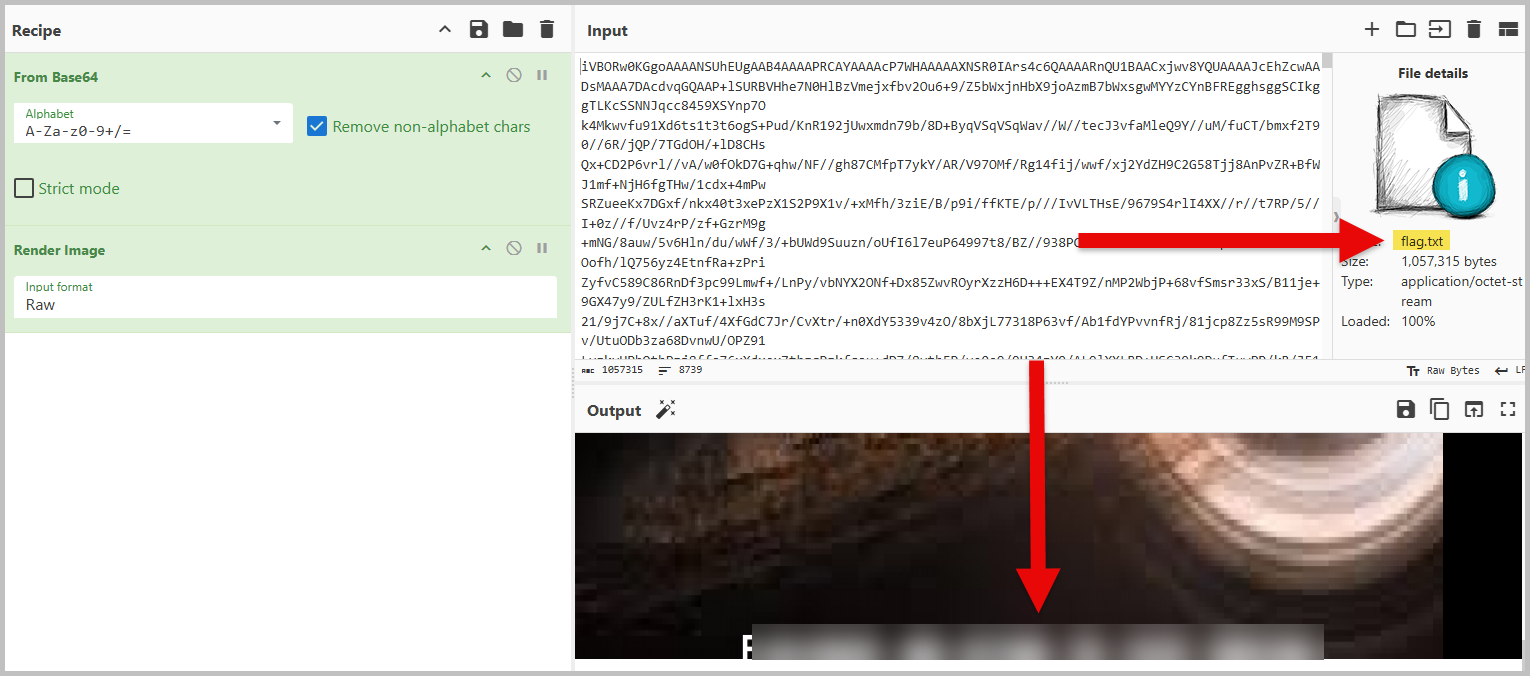
Hope this helps. Love this challenge. I spent longer than I was expecting. Embarassing confession, it took me a good ten minutes to finally enter the correct flag. The font of the flag made it difficult for me. I had to try different combinations. Haha.
Well done
LikeLiked by 2 people